Description
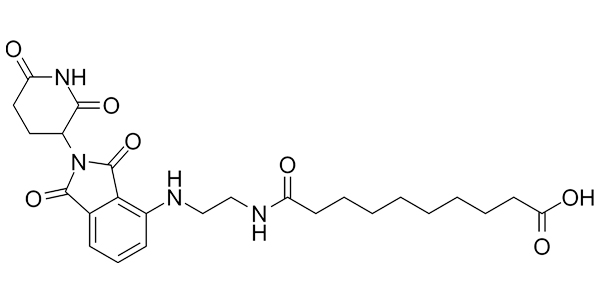
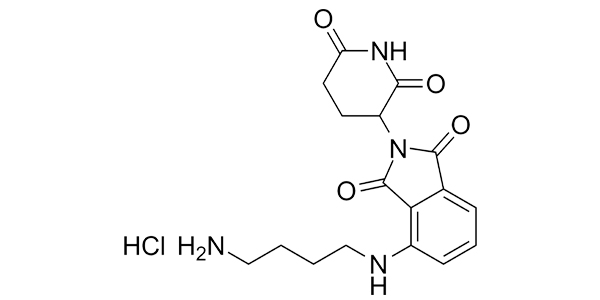
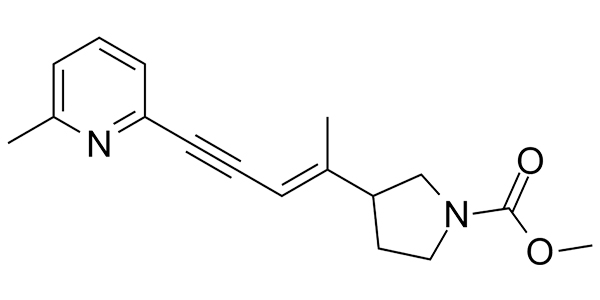
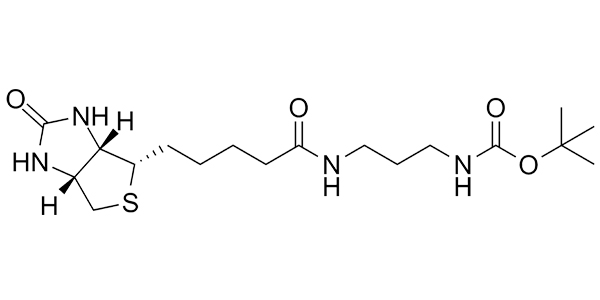
This compounds has uses in synthesis of potential drug candidates and as a negative control in biochemicals assays.
$620.00 – $4,820.00
This compounds has uses in synthesis of potential drug candidates and as a negative control in biochemicals assays.
Room temperature free S&H from Ann Arbor, MI. Shipping on ice packs available upon request.
Storage stability not tested. Recommended storage at -20°C.
≥ 1 year
Christian Steinebach,a,‡ Yuen Lam Dora Ng,b,‡ Izidor Sosič,c Chih-Shia Lee,d Sirui Chen,b Stefanie Lindner,b Lan Phuong Vu,a Aleša Bricelj,c Reza Haschemi,e Marius Monschke,f Elisabeth Steinwarz,e Karl G. Wagner,f Gerd Bendas,e Ji Luo,d Michael Gütschow, a and Jan Krönke
a and Jan Krönke b
b
Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (CDK6) is an important regulator of the cell cycle. Together with CDK4, it phosphorylates and inactivates retinoblastoma (Rb) protein. In tumour cells, CDK6 is frequently upregulated and CDK4/6 kinase inhibitors like palbociclib possess high activity in breast cancer and other malignancies. Besides its crucial catalytic function, kinase-independent roles of CDK6 have been described. Therefore, targeted degradation of CDK6 may be advantageous over kinase inhibition. Proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) structurally based on the cereblon (CRBN) ligand thalidomide have recently been described to degrade the targets CDK4/6. However, CRBN-based PROTACs have several limitations including the remaining activity of immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) on Ikaros transcription factors as well as CRBN inactivation as a resistance mechanism in cancer. Here, we systematically explored the chemical space of CDK4/6 PROTACs by addressing different E3 ligases and connecting their respective small-molecule binders via various linkers to palbociclib. The spectrum of CDK6-specific PROTACs was extended to von Hippel Lindau (VHL) and cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1 (cIAP1) that are essential for most cancer cells and therefore less likely to be inactivated. Our VHL-based PROTAC series included compounds that were either specific for CDK6 or exhibited dual activity against CDK4 and CDK6. IAP-based PROTACs caused a combined degradation of CDK4/6 and IAPs resulting in synergistic effects on cancer cell growth. Our new degraders showed potent and long-lasting degrading activity in human and mouse cells and inhibited proliferation of several leukemia, myeloma and breast cancer cell lines. In conclusion, we show that VHL- and IAP-based PROTACs are an attractive approach for targeted degradation of CDK4/6 in cancer.